IBM’s data breach report is a leading cyber security report. In its 17th year edition, it has unveiled some of the most surprising impacts of a data breach in the current and past years. It offers IT managers and security leaders plenty of insight into the factors that help mitigate the rising cost of data breaches.
This report presents a thorough overview of 537 legitimate data breaches that happened in 17 countries and 17 different industries. When formulating this report, experts conducted 3500 interviews in which they asked the organizations about their response in the face of a data breach, the practices they used to limit damage, and how effective those practices were.
This summary of the report is categorized similarly to the five major sections that you can find on the report. These sections include:
- Key findings of the report
- A dive into the chart analysis
- The methodology involved in quantifying the risk
- Security tips and recommended prevention tactics can help organizations control their financial losses in the face of a breach.
- Some comments on characteristics that were involved in this study
Key Findings
- Between 2020 and 2021, the damaging costs of a data breach increased by a whopping 10%. This is the largest cost increase that has been recorded in a single year. An increase was seen from 3.86 million dollars to $4.24. On the individual organization level, the costs were lower for companies that have good security frameworks, and lower for companies that did not pay much attention to security.
- The average cost of a data breach for mega-breaches multiplied 100x, estimating around $401 million. In a sample of mega breaches ranging from 1 million to 65 million records, the giant data breaches were vastly more costly than the average cost of the smaller ones. The data breaches between 50 million and 65 million records accounted for a price that was a hundred times more expensive than the rest of the sample. This shows that a smaller number of organizations suffered incredibly more than the majority in the sample.
- A Zero Trust Approach Worked Best in reducing data breach cost. The companies that deployed a zero-trust approach to their cyber security experienced a data breach damage of about 5 million. This showcases that a zero-trust approach worked significantly greater for companies that did not have it deployed. This resulted in a difference of 2.3%
- Security AI and automation were most effective. Organizations that were equipped with artificial intelligence technologies and automation methods had an upper hand when it came to minimizing risks. The companies that deployed AI integrated security experienced a breach of only 2.9 million dollars, whereas, the organizations that did not have artificial intelligence-backed security technologies suffered 6.71 million in data breach costs. The security AI deployment resulted in a faster identification and recovery time in the instance of a breach.
- Between all the cloud types, the hybrid cloud model resulted in the lowest average cost in a data breach. The hybrid cloud model proved to be one of the best cloud integrations for organizations in the face of a data breach. It performed better than the on-premise, public, and private cloud deployment models.
Another factor that determined the breach cost was the migration stage. Companies that were in the middle of the migration phase suffered more than the ones which are in the mature stages of cloud migration. The organizations that are further into modernization maturity detected malicious activity 77 days faster.
- Compliance failures and complexity were the most integral factors that increased data breach costs. Organizations that had complex systems experienced more losses due to data breaches than others. Another common factor that resulted in more damage to the data breach was compliance failure.
- Ransomware was more damaging than other types of breaches and malware. Ransomware attacks are estimated to be four million dollars of company expenses. This cost is excluding the ransom payments that companies had to pay. It instead includes the downtime costs, response costs, infrastructure damage, and more. The destructive attacks, which corrupt data, cost about 4.69 million dollars. About 7.8% of companies experienced ransomware attacks as a breach.
A Dive into Chart Analysis
The key findings of the report are supported with chart analysis and extensive statistical finds. This report pertaining to the cost of a data breach is global. Nonetheless, for a better understanding, the report also singles out the data results of specific countries and regions for comparative purposes.
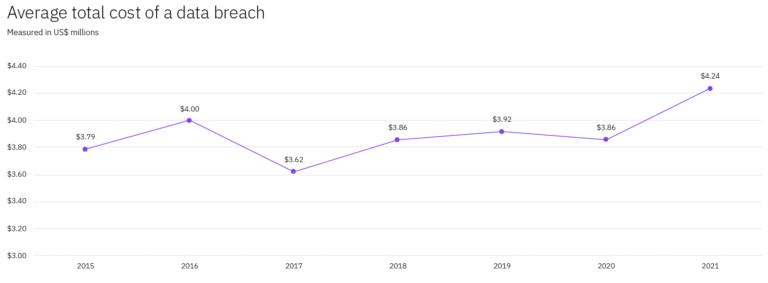
From this graph, it is evident that the data breach costs have grown significantly since 2015. To be precise, it has increased by a margin of 11.9% from 2015 to 2021.
Average Cost Of Data Breach In terms of Countries and Regions
The United States topped the chart in regards to global data breach costs. The countries and regions that followed the United States and made the top 5 list were the Middle East in second place with a data breach cost of $6.93 million. Following that is Canada who falls in third place, suffering from a data breach cost of $5.40 million. Germany fell in fourth place and Japan was unfortunate to make fifth place. The only region that witnessed a cost decrease was Brazil, which impressively lowered its data breach cost by 3.6%.
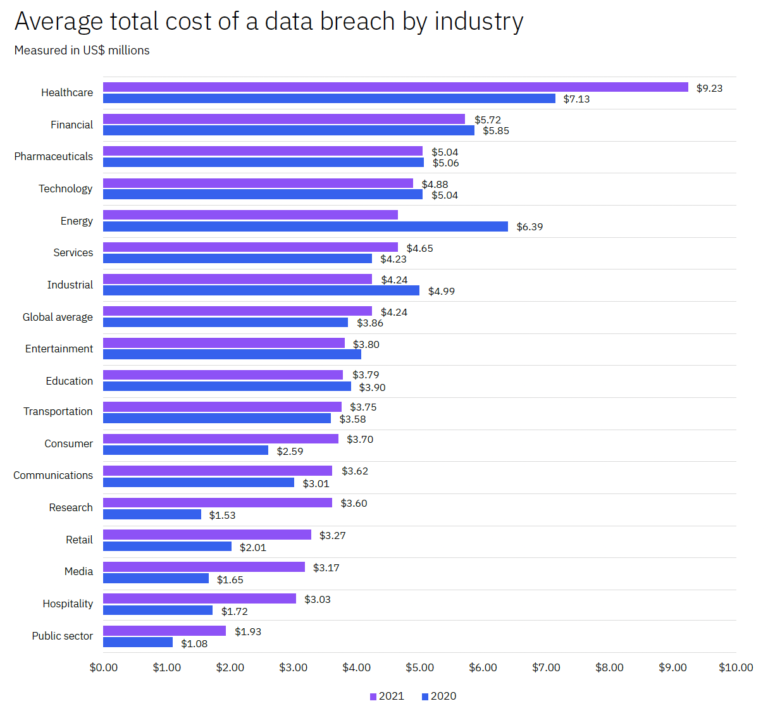
The average data breach damage for the healthcare industry witnessed a 29.5% increase in the span of a year. On the other hand, the energy sector saw an improvement in its cyber security as it fell from second place in 2020 to fifth place with a 27.2% decrease from 2020 to 2021. Other industries experienced an increase in cyber security breaches.
Attack Vectors
This part of the report pertains to the type of attack which caused the highest data breach. The study divides these breaches into 10 initial attacks. These attacks range from compromised cloud configurations, phishing threats to stolen credentials. A key finding in this study was that the average cost of a data breach that compromised business emails and credentials was 5 million.
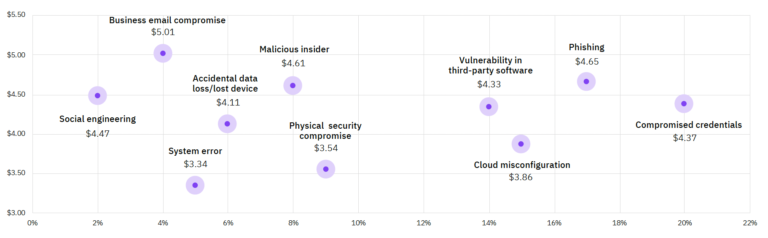
The most common cyber attack in 2021 came from compromised credentials. About 20% of the data breach involved intruder access and exposure to business emails, passwords, and credentials. Phishing is the second most common attack vector and moved up to second place in 2021, from its fourth position in 2020.
What is Phishing and Cloud Misconfiguration Attacks?
Phishing is a cyber-attack method, in which a hacker tries to get hold of personal information using deceptive websites and emails. This is a sophisticated method of breaching data. When conducting this attack, the goal of a phishing attempt is to deceive a subject into believing that an email or website is legitimate and urgent.
This for instance can be a message from an associate or company which will request the recipient to download attachments, enter their credentials or simply click on a link. The analogy of the term Phish portrays an angler or an attacker throwing a hook in the large pool of the web with bait and waiting to catch someone.
A Cloud misconfiguration attack is an attempt of the hacker to find vulnerabilities and holes in an organization’s cloud configuration and exploit them to breach important data. Migrating to the cloud essentially means that a company has to move its procedural infrastructure to a virtual platform.
This puts their data at risk and hackers are finding innovative ways to attack organizations. According to this report, they especially attack entities that are in the early stages of cloud migration.
Regulatory Compliance Failures
This year’s research studied the failures of regulatory compliance and the numbers deduced explains that the average total cost of a data breach due to compliance failures was the highest amongst all factors. What this means is that organizations that follow cyber security regulations and requirements are more successful in minimizing the cost damage.
The definition of compliance in IT is the act of adhering with state regulations. There are several major regulations that organizations must comply with and these regulations reflect common issues of different industries. For instance, industries such as healthcare, finance, or defense have common problems when it comes to cyber security.
Below, a graph from the report shows the data breach costs overtime in high VS low regulatory environments.
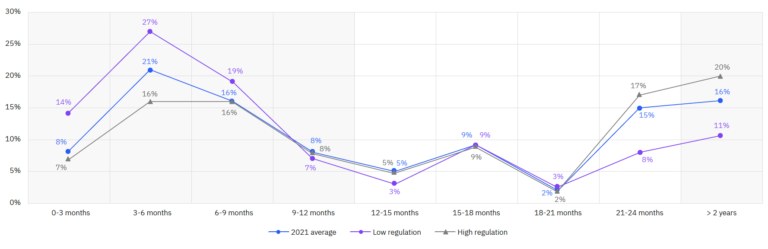
This graph clearly shows that organizations functioning in high regulatory environments were able to sustain their data breach costs over two years far better than companies functioning in low regulatory environments.
Impact of Zero Trust
This part of the study looked closely at organizations that deployed zero trust security architecture. Zero trust is a security strategy that explains you should not implicitly trust any user, application, or device with company data. It is not something that you can deploy by introducing new technology. It is neither a buyable service or product.
It is instead a methodology that allows companies to strategize their cyber security. It is also a shift away from perimeter security. This is the notion which reflects a boundary wall around an organization for protection against malicious activities. This can only work as long as all business operations happen inside business premises.
Since employees are now working flexibly from different places and sharing data across hybrid cloud platforms, perimeter security is no longer viable. In addition to that, attackers are finding it easier than ever to exploit credentials by disguising themselves as trustworthy.
In an environment such as this, the zero trust principle enables security for organizations by never trusting users and only relying on verifications. Every time an employee or worker attempts to access a database or make connections to the system, they will have to go through various authorizations and authentications.
The zero trust architecture also grants minimum access to devices and recipients working on the network. The report unveiled that only a third of organizations have a fully deployed or partially deployed a zero-trust approach. The data breach costs stayed significantly lower for organizations that rely on a mature stage of the zero-trust procedure. Below is a chart from the report which displays this.
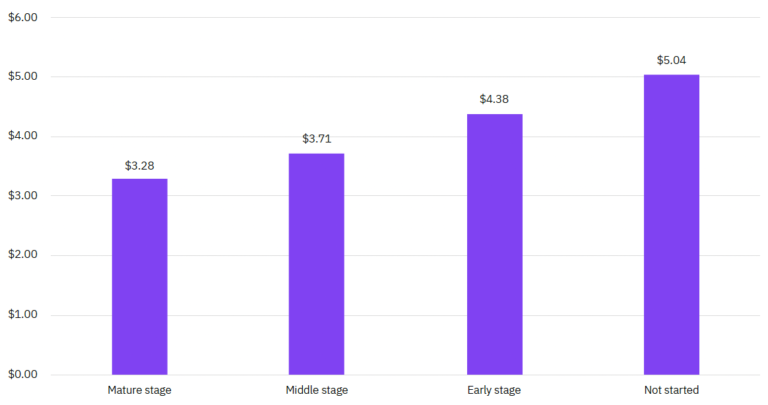
According to this chart, the average cost of a data breach for organizations that did not rely on the zero-trust approach was 5.04 million dollars. While on the other hand, companies that had deployed zero-trust architecture suffered a breach cost of 3.28 million dollars. The difference between the costs is 42.3%. Moreover, the difference between the data breach costs of organizations at an early stage of zero trust, and organizations at a mature stage is 28.7%.
Security recommendations
According to the findings regarding the data breach costs, security threats, and best recovery practices, the report concludes by recommending the best practices for protection against security threats. These practices include:
- Investing in security automation and AI integrations to increase the speed of detection and response to data – The study concluded that automation and security AI incorporations were most significant in reducing the data breach costs.
- Stress testing incident response plan – In the study, the organizations that were equipped with an incident response or IR teams experienced fewer data breach costs. Incident response testing refers to testing out the security system by trying to attempt an attack and observing how quickly the system responds.
- Deploying zero-trust model – Organizations that had a mature and full-proof zero trust system in place were able to mitigate risks and limit their data breach costs against ones that didn’t.
- Investing in governance, risk management programs – The study revealed government regulatory compliance, framework for audits, and the Fair risk quantification method as one of the best ways to improve cyber security.
- Using policy and encryption techniques for data protection in the cloud – As the world turns towards the cloud and database storage and business functions, it allows attackers a unique opportunity for a breach. Solidifying the security of the cloud is thus a critical step for protection.
- Minimizing IT complexity – This year’s study also showed how IT complexity can be a contributing factor to high data breach costs. One of the best ways to resolve this threat is by hiring a managed security service provider which simplifies all security infrastructure and proceedings into a single platform.
References:


